Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP. In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell. The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells.
Autotrophs like plants produce glucose during photosynthesis. But cellular respiration is slightly more complicated than just converting the energy from glucose into ATP. Hydrolysis Breaking a bond in a molecule and splitting it into smaller molecules through a reaction with water.
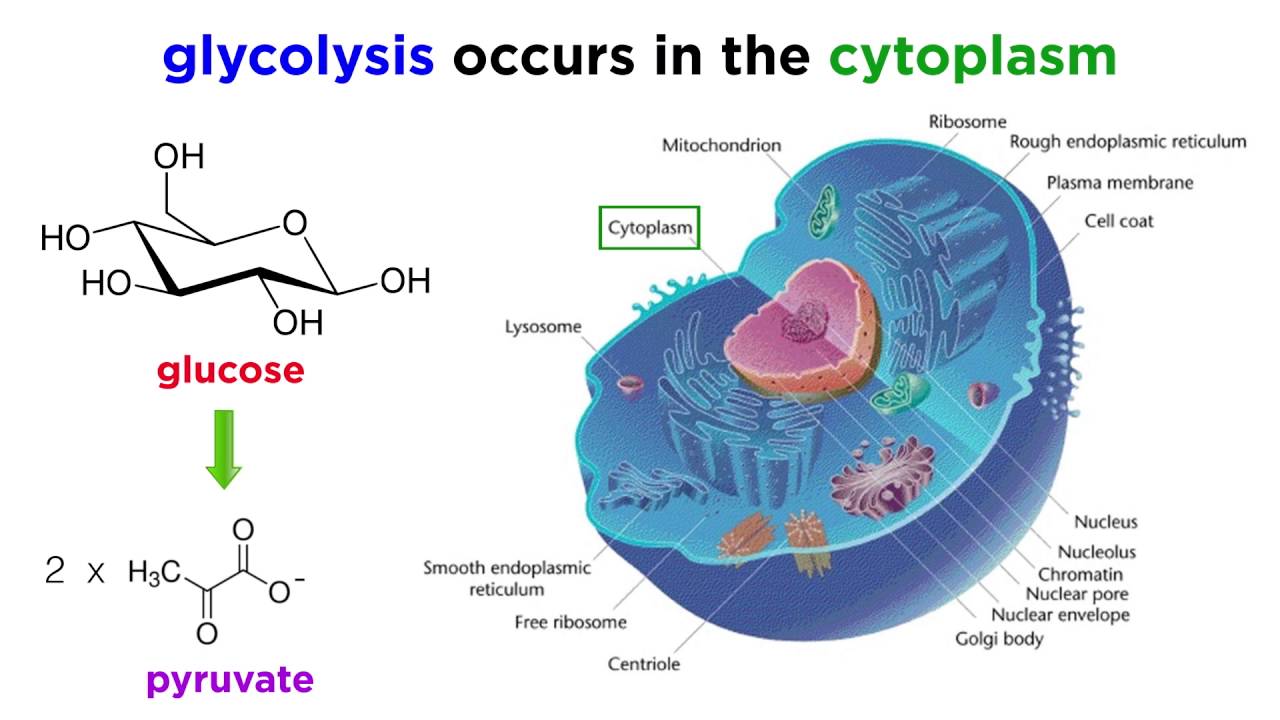
Introduction to Cellular Respiration. Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. Refer to the image below for a quick overview of the process taking place during this respiration.
Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation.
The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell. In this process glucose is broken down in the presence of molecular oxygen into six molecules of carbon dioxide and much of the energy released is preserved by turning ADP and free phosphate into ATP. Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism.
Heterotrophs like humans ingest other living things to obtain glucose. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.