Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

Xylem present in the vascular plants is made of cells that provide structural.
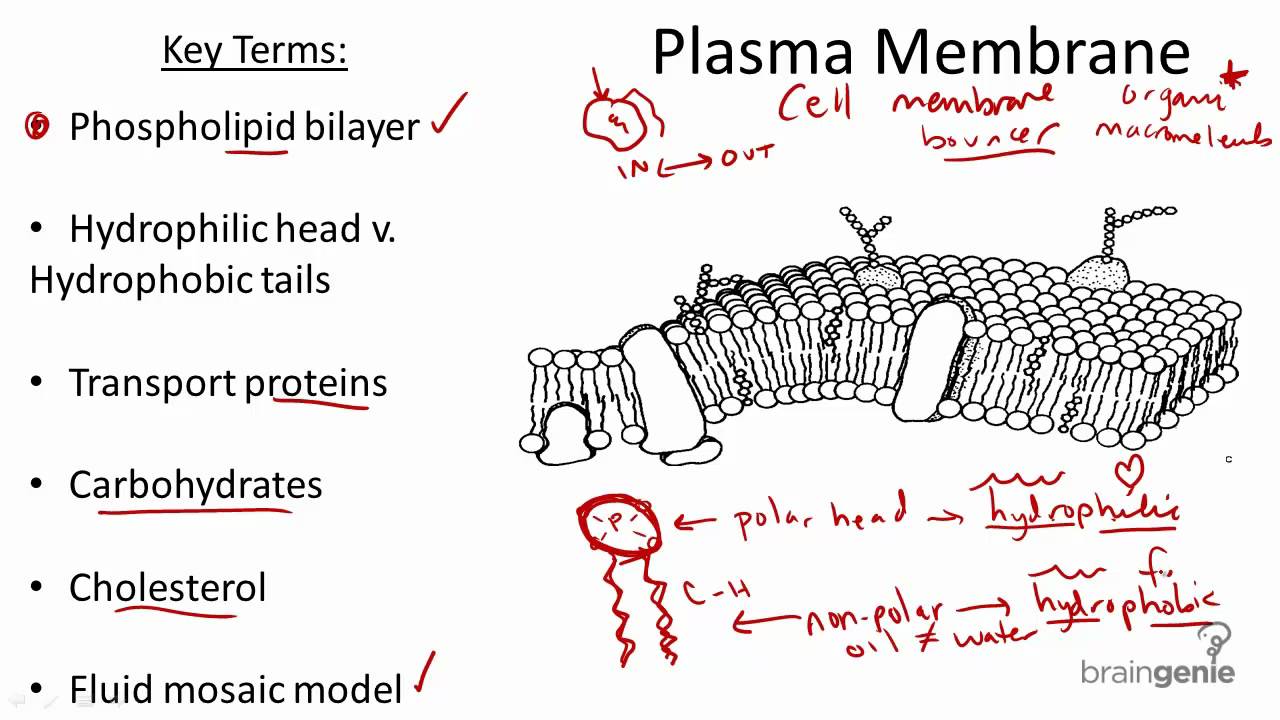
Cell membrane structure and function a level. Much of the membrane is made up of a sea of phospholipids with protein molecules floating in between the phospholipids. Contains chromosomes DNA code for the synthesis of proteins that control the function of the cell hence the nucleus commands the cell Cell Surface membrane. The liquid where all.
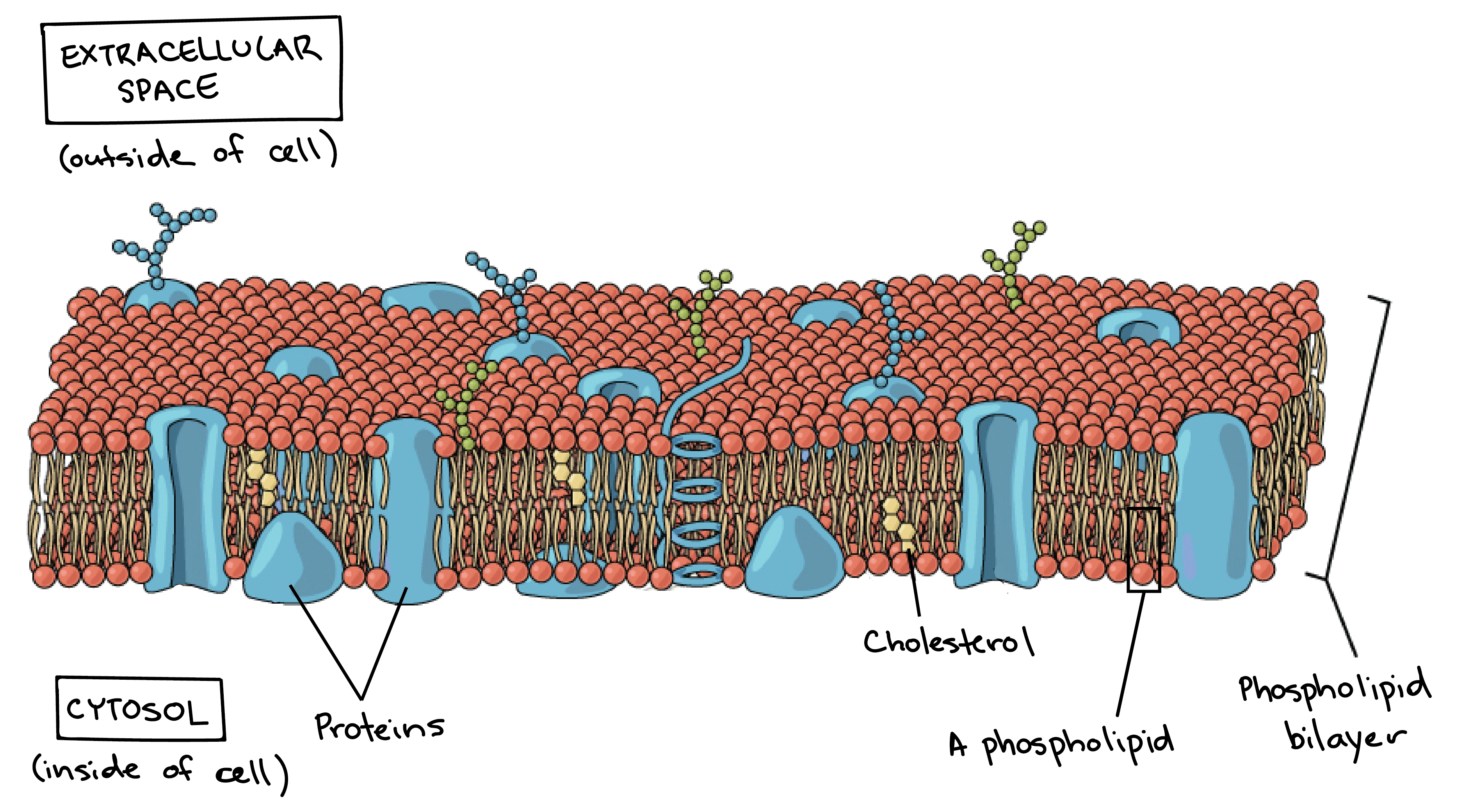
The membrane also contains membrane proteins including integral proteins that go across the membrane serving as membrane. It is a fluid mosaic of lipids proteins and carbohydrate. The membrane is examined in detail later.
Cell Membranes a outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells b state that plasma cell surface membranes are partially permeable barriers Plasma membranes are partially permeable meaning they let some molecules through but not others. Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell in animals. Some of these proteins span the whole width of the membrane.
Organelles perform different functions within a cell and this is called the Division of Labour. This is a thin flexible layer round the outside of all cells made of phospholipids and proteins. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes.
Membranes formed from phospholipid bilayers help to compartmentalise different regions within the cell as well as forming the cell surface membrane Exam Tip An example of a membrane-bound organelle is the lysosome found in animal cells each containing many hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many different kinds of biomolecule. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer including cholesterols that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity at various temperatures. The separation of different parts of the cell with different functions by using membranes is called compartmentalisation providing distinct conditions for different processes.
-A double membrane sac which pinches off the end of organelles such as the RER or Golgi Apparatus and fuses with other membranes such as the RER Golgi or Plasma Membrane Function of Vesicles -Transport proteins and other substances between organelles and the outside of the cell. 1 Isolate cells contents from outside environment 2 Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3 Communicate with other cells Note. Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane.